Finite element simulation and experiment study on exciting quasi-SH wave circumferentially in the casing
Abstract
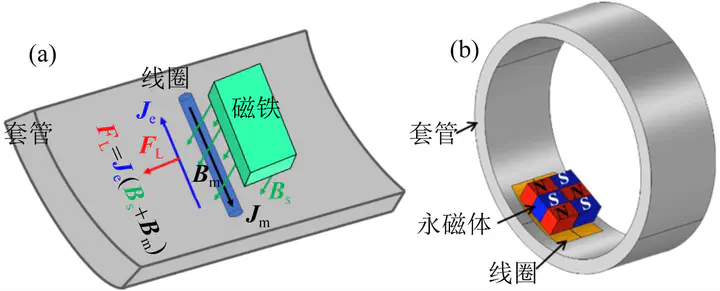
For acoustic logging methods in a cased well,the conventional working pattern is that the acoustic wave is excited in the mud and radiates into the casing,and then the casing wave isinduced.This way is not efficient in heavy-weight or gassy mud.This paper introduces the electromagnetic acoustic transducer (EMAT) based on Lorentz force mechanism into the cased well. The advantagesof EMAT are that the quasi-SH waves can be induced in the casing directly without acoustic coupling between mud and casing. The quasi-SH waves are polarized in the axial direction and propagates circumferentially.Combining the COMSOL finite element simulation the Lorentz force type electromagnetic ultrasonic transducers are designed and optimized. Quasi-SHO and higher modes can be excited in the casing. The electromagnetic ultrasonic transducers based on the simulation results recorded the SH waves propagating circumferentially along the casing in the laboratory. In a well-bonded well, quasi-SH waves propagate along the casing circumferentially and leak energy into the cement behind the casing, and the leak quasi-SH waves can be reflected at the interface between cement and formation. Then the reflected waves can be coupled into the casing and received by the receivers. In hard and soft formation cased well models, the reflected waves are in opposite phases. Comparing with direct waves, the phase changes of reflected waves fully verify the propagation characteristics of quasi-SH waves.