Stoneley wave reflection and transmission across permeable formations and fractured zones:Comparison of analytical and numerical modeling results
Abstract
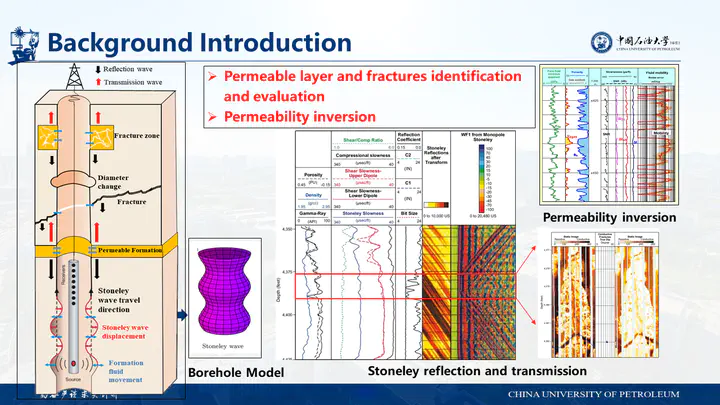
Borehole Stoneley waves are commonly used to evaluate reservoir permeability and identify formation fractures. The propagation of acoustic waves in permeable formations requires solving the Biot’s poro-elastic wave equations. The finite difference method is used to solve the problem of Stoneley wave reflection and transmission across permeable formations and fracture zones. In this article, the finite difference method and one-dimensional effective wavenumber method were collectively applied to study and analyze the Stoneley wave reflection and transmission coefficients and their variation characteristics with different thickness, permeability and porosity of porous formations. The results verify the reliability of the effective wavenumber method in the range of 0-2kHz. An advantage of the finite difference method is to solve the more complex fractures zone problem that is difficult for the wavenumber method, analyzing the Stoneley wave reflection and transmission coefficients for different permeability, porosity, and axial and radial extension length parameters. The main results of this paper show that the Stoneley-wave induced fluid flow in the zone is a skin effect having a limited depth of penetration. Thus, to measure the fluid flow effect beyond a radial depth of, say 0.1m, one should use a low-frequency band of 0-2kHz, in which both the Stoneley wave reflection and transmission coefficients are sensitive to the fluid transport property of the zone in the borehole vicinity. In general, the Stoneley-wave reflection coefficient increases significantly at low frequencies, and the transmission coefficient decreases with increasing frequency. However, when the wave frequency is close to Biot characteristic frequency, the reflection and transmission coefficient show complicated variation trend with increasing frequency and permeability, due to dynamic fluid flow characteristics in the fracture zone. The methods and results in this paper are helpful to analyze and evaluate the propagation characteristics of Stoneley waves in fractured permeable formations.